Let's get acquainted with design thinking!!!
As teachers, we have a noble task, educating and teaching knowledge to our students. To be able to do both optimally, we need certain ways and methods that can help us in teaching, starting from the preparation, the process, and the final result. Education is dynamic, so the methods that we apply must also be used according to advances of science and technology. Design Thinking (DT) is present as a method and base knowledge that invites us to think systematically, logically, factually, and based on data. This method has long been applied in other countries, especially developed countries, but in Indonesia the term design thinking is still not popular and many people, especially teachers, do not know what DT is. After learning DT, it is hoped that teachers have a more important awareness of data so that we can design the lessons that are suitable for the conditions of our students. Let's learn Design Thinking in this blog.
1. DESIGN THINKING is an iterative process in which we seek to understand the user, challenge assumptions, and redefine problems in an attempt to identify alternative strategies and solutions that might not be instantly apparent with our initial level of understanding. At the same time, it provides a solution-based approach to solving problems. It is a way of thinking and working as well as a collection of hands-on methods. Design Thinking revolves around a deep interest in developing an understanding of the people for whom we’re designing the products or services. It helps us observe and develop empathy with the target user. Design Thinking helps us in the process of questioning: questioning the problem, questioning the assumptions, and questioning the implications. Design Thinking is extremely useful in tackling problems that are ill-defined or unknown, by re-framing the problem in human-centric ways, creating many ideas in brainstorming sessions, and adopting a hands-on approach in prototyping and testing. By using this thinking method, “maker mindset” can grow to the designer or people because several steps appear in this process. Starting from empathize, define, ideate, prototype and test.
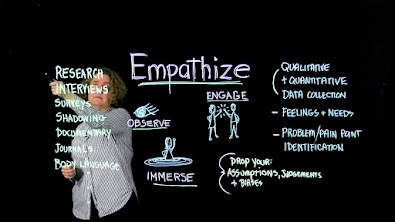
EMPATHIZE
Empathize is the first step to collect data about the users. The purpose in this step is for understanding the problem. Asking the right questions can be very crucial within this step. By asking the right questions, we can learn about the audience for whom we are designing. To conduct this step, there are some ways that can be done such as interviewing, observing, researching, etc. The awareness that appear after conducting this step is feeling to be immersed and engage with the users. We have to avoid assumptions, judgements, and biases. Remember, we work with the data.
DEFINE
The second step is define. After data is being collected from the step of empathize, we gather all those data into information. The purpose within this step is collecting the information gained, then we analyze all the information, re-frame it, choose the appropriate one, synthesize into insight and the needs (user's goals). This important insight and needs can be used to develop problem statement (what exactly the problem is) to create an innovative solution.
IDEATE
Ideate is the third step in DT. It is time for us to arrange the notes we have into idea. This step involves our brainstorming large quantities of ideas and creative solutions by combining our imagination with the information gathered from the empathy work to move towards prototyping. We also have to identify multiple ideas for prototyping based on how well the ideas would likely meet the criteria for success.
PROTOTYPE
The fourth step is prototype. In this step, we build a representation of one or more of our ideas to show to others. We undergo an iterative process of creating and improving prototypes with the experience that can be utilized by the users. Feedback is necessary to improve the product before released. After getting feedback, iteration can be done in the previous step if it is needed until we got the best product based on the users need.
TEST
j The final step is testing the product. In this step, we provides users with our prototype to use in a realistic situation. The interaction between the users and the designers will create a new insights and ideas that can help to improve the next iteration of prototypes.






No comments:
Post a Comment